Leptospirosis
Background
- Human exposure from animal urine, contaminated water/soil, or infected animal tissue.
- Portal from break in skin, mucousa, or conjunctiva
- Average incubation of 10 days
Clinical Manifestations
- fvr, myalgia, ha (75-100% of pts)
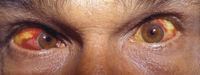
- conjuntival suffusion characteristic but not common
- meningitis, uveitis, transminitis, proteinuria, hematuria
- Weil syndrome-severe manifestation with jaundice and renal failure, pulmonary hemorrhage, ARDS, myocarditis, and rhabdomyolysis (52% Mortality)
Laboratory findings
- Confirm by serology
- Culture
- Hypokalemia/Hyponatremia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Sterile pyuria
- Elevated CK
- CSF with elevated wbcs and protein with normal glucose
Differential Diagnosis
Fever in traveler
- Normal causes of acute fever!
- Malaria
- Dengue
- Leptospirosis
- Typhoid fever
- Typhus
- Viral hemorrhagic fevers
- Chikungunya
- Yellow fever
- Rift valley fever
- Q fever
- Amebiasis
- Zika virus
Treatment
- Ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, PCN, azithromycin, or doxycycline
- Prefer azithro or doxy if unable to distinguish from rickettsial infection.
- Beware of Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction
Source
- Palaniappan RU, Ramanujam S, Chang YF. Leptospirosis: pathogenesis, immunity, and diagnosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2007;20(3):284-92