Diferencia entre revisiones de «Hydrocephalus»
Sin resumen de edición |
Sin resumen de edición |
||
| Línea 3: | Línea 3: | ||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
*[[Headache]] | *[[Headache]] | ||
*[[Diplopia]] | *[[Diplopia]] | ||
| Línea 11: | Línea 9: | ||
*[[Nausea and Vomiting]] | *[[Nausea and Vomiting]] | ||
*[[Altered Mental Status]] | *[[Altered Mental Status]] | ||
*Irritability | *Peds (in addition to above): | ||
*Increased lower extremity tone | **Large fontanelles | ||
*Remember that Babinski sign is normal up to 3 years of age | **Dilated scalp veins | ||
**Irritability | |||
**Increased lower extremity tone | |||
**Remember that Babinski sign is normal up to 3 years of age | |||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
Revisión del 03:25 17 feb 2016
Background
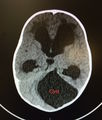
Hydrocephalus is caused by excessive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulation often from an obstructive process such as CSF shunt malfunction or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Patients can also suffer from nonobstructive hydrocephalus due to excessive production of CSF.[1]
Clinical Features
- Headache
- Diplopia
- Ocular Palsy - 6th nerve palsy, strabismus
- Papilledema
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Altered Mental Status
- Peds (in addition to above):
- Large fontanelles
- Dilated scalp veins
- Irritability
- Increased lower extremity tone
- Remember that Babinski sign is normal up to 3 years of age
Differential Diagnosis
Workup
- Physical Exam to assess for papilledema or neuro defects
- CT Brain non contrast
Management
Disposition
See Also
External Links
Sources
- ↑ Shprecher D. et al. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: diagnosis and treatment. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2008;8(5):371-376.