Diferencia entre revisiones de «Flexion cervical teardrop fracture»
(added ref section) |
(→Workup) |
||
| Línea 13: | Línea 13: | ||
{{Cervical spine injuries}} | {{Cervical spine injuries}} | ||
== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
*Cervical xrays or CT | |||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
Revisión del 13:01 19 dic 2015
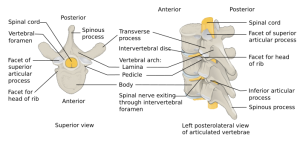
Background
- Is an unstable spine injury
Clinical Features
- Severe flexion > vertebral body colliding with the one below (shallow water diving injury, MVC deceleration)
- Most commonly at C5-C6
- Displacement of teardrop shaped fragment of antero-inferior portion of superior vertebra
- Leads to posterior displacement of vertebral body and disruption of posterior longitudinal ligament
- Frequently occurs with spinal cord injury[1]
- Associated with acute anterior cervical cord syndrome
Differential Diagnosis
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Diagnosis
- Cervical xrays or CT
Management
Prehospital Immobilization
See NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization
Hospital
- C-collar
- Consult ortho or spine as needed
Disposition
- Admit
See Also
References
- ↑ Fujimura, Y., Nishi, Y., Chiba, K. and Kobayashi, K. (1995) ‘Prognosis of neurological deficits associated with upper cervical spine injuries’, Spinal Cord, 33(4), pp. 195–202.