Diferencia entre revisiones de «Cervical burst fracture»
Sin resumen de edición |
|||
| Línea 7: | Línea 7: | ||
**Compromise of >50% of spinal canal | **Compromise of >50% of spinal canal | ||
**Axial compression > nucleus pulposus forced into vertebral body | **Axial compression > nucleus pulposus forced into vertebral body | ||
{{Vertebral fractures and dislocations types}} | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
| Línea 13: | Línea 15: | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
==Evaluation== | ==Evaluation== | ||
| Línea 20: | Línea 22: | ||
**AP x-ray - Vertical fracture of the body | **AP x-ray - Vertical fracture of the body | ||
**Consider MRI - posterior ligament often injured | **Consider MRI - posterior ligament often injured | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Prehospital Immobilization see [[EBQ:Prehospital Spine Immobilization|NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization]] | *Prehospital Immobilization see [[EBQ:Prehospital Spine Immobilization|NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization]] | ||
Revisión del 13:11 24 oct 2020
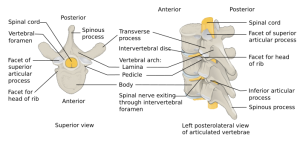
Background
- For C1 burst fracture, see Jefferson fracture
- Unstable if:
- Associated neurologic deficits
- Loss of >50% of vertebral body height
- >20 degrees of spinal angulation
- Compromise of >50% of spinal canal
- Axial compression > nucleus pulposus forced into vertebral body
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Clinical Features
- Neck pain in the setting of trauma
- Complete or incomplete spinal cord injury common
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
- Imaging
- Lateral x-ray - Comminuted body and loss of vertebral height
- AP x-ray - Vertical fracture of the body
- Consider MRI - posterior ligament often injured
Management
- Prehospital Immobilization see NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization
Disposition
- Generally admit