Diferencia entre revisiones de «Hip dislocation»
(added backgound) |
|||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
*Orthopedic emergency; reduction should occur w/in 6hr | *Orthopedic emergency; reduction should occur w/in 6hr | ||
*High risk of AVN | |||
*High-energy trauma is primary mechanism | *High-energy trauma is primary mechanism | ||
*Types: | *Types: | ||
Revisión del 14:52 29 dic 2014
Background
- Orthopedic emergency; reduction should occur w/in 6hr
- High risk of AVN
- High-energy trauma is primary mechanism
- Types:
- Posterior
- 90% of hip dislocations
- Acetabular fractures may result as well
- Anterior
- 10% of hip dislocations
- Can be superior (pelvic) or inferior (obturator)
- Neurovascular compromise is unusual
- Posterior
Clinical Features
- Posterior Dislocation
- Extremity is shortened, internally rotated, adducted
- Anterior Dislocation
- Extremity is flexed, externally rotated, abducted
- Similar to hip fracture
Imaging
- Hip AP and lateral views
- Also consider Judet views or CT to evaluate acetabulum (esp for posterior dislocation)
Management
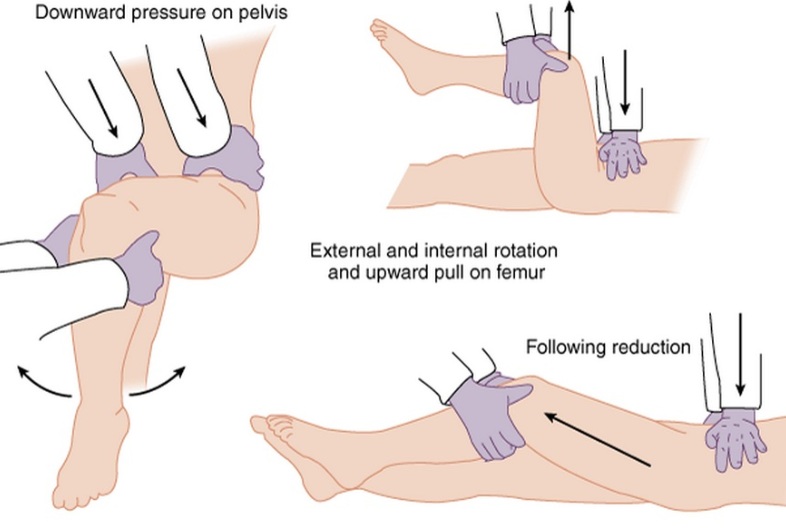
- Reduce
Source
- Tintinalli