Diferencia entre revisiones de «Leptospirosis»
| Línea 24: | Línea 24: | ||
==Treatment<ref> [http://www.moh.gov.my/images/gallery/Garispanduan/GL_Leptospirosis%202011.pdf Ministry of Health Malaysia 2011 Recommendations</ref> == | ==Treatment<ref> [http://www.moh.gov.my/images/gallery/Garispanduan/GL_Leptospirosis%202011.pdf Ministry of Health Malaysia 2011 Recommendations</ref> == | ||
[[Penicillin|PCN]] | |||
*Penicillin G 100000U/ kg/ dose IV every 6 hours x 7days | |||
OR | |||
#'''>8yrs:''' Doxycycline 4mg/kg/dose oral every 12 hours x 7 days | |||
#'''<8yrs:''' [[Ampicillin]] 75-100mg/kg/dose oral every 6 hours x 7days | |||
#'''<8yrs:''' [[Amoxicillin]] 50mg/kg/dose oral 6- 8 hours x 7days | |||
Alternatives: | |||
#[[Ceftriaxone]], [[Cefotaxime]]<ref>Inada R, Ido Y, Hoki R. The etiology, mode of infection, and specific therapy of Weil's disease (spirochaetosis icterohaemorrhagica. J Exper Med. 1916;23:377-402.</ref> | |||
*''Prefer [[Azithromycin]] or [[Doxycycline]] if unable to distinguish from rickettsial infection.'' | |||
*Be aware of the potential for a [[Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction]] | |||
==Source== | ==Source== | ||
Revisión del 17:51 7 jun 2014
Background
- Human exposure from animal urine, contaminated water/soil, or infected animal tissue.[1]
- Portal from break in skin, mucousa, or conjunctiva
- Average incubation of 10 days
- Also described following hiking, trekking, and following triathlon competitions[2]
Clinical Manifestations
- Fever, Myalgias, Headaches (75-100% of pts)
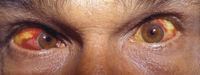
- Conjuntival suffusion characteristic but not common
- Meningitis, uveitis, transminitis, proteinuria, hematuria
- Weil syndrome-severe manifestation with jaundice and renal failure, pulmonary hemorrhage, ARDS, myocarditis, and rhabdomyolysis (52% Mortality)
Laboratory findings
- Confirm by serology
- Culture
- Hypokalemia/Hyponatremia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Sterile pyuria
- Elevated CK
- CSF with elevated wbcs and protein with normal glucose
Differential Diagnosis
Fever in traveler
- Normal causes of acute fever!
- Malaria
- Dengue
- Leptospirosis
- Typhoid fever
- Typhus
- Viral hemorrhagic fevers
- Chikungunya
- Yellow fever
- Rift valley fever
- Q fever
- Amebiasis
- Zika virus
Treatment[3]
- Penicillin G 100000U/ kg/ dose IV every 6 hours x 7days
OR
- >8yrs: Doxycycline 4mg/kg/dose oral every 12 hours x 7 days
- <8yrs: Ampicillin 75-100mg/kg/dose oral every 6 hours x 7days
- <8yrs: Amoxicillin 50mg/kg/dose oral 6- 8 hours x 7days
Alternatives:
- Prefer Azithromycin or Doxycycline if unable to distinguish from rickettsial infection.
- Be aware of the potential for a Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction
Source
- Palaniappan RU, Ramanujam S, Chang YF. Leptospirosis: pathogenesis, immunity, and diagnosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2007;20(3):284-92
- ↑ Radl C. et al. Outbreak of leptospirosis among triathlon participants in Langau, Austria, 2010. Wien Klin Wochenschr. Dec 2011;123(23-24):751-5
- ↑ CDC. Update: leptospirosis and unexplained acute febrile illness among athletes participating in triathlons--Illinois and Wisconsin, 1998. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1998;47(32):673-6
- ↑ [http://www.moh.gov.my/images/gallery/Garispanduan/GL_Leptospirosis%202011.pdf Ministry of Health Malaysia 2011 Recommendations
- ↑ Inada R, Ido Y, Hoki R. The etiology, mode of infection, and specific therapy of Weil's disease (spirochaetosis icterohaemorrhagica. J Exper Med. 1916;23:377-402.