Diferencia entre revisiones de «Tar burn»
Sin resumen de edición |
(Prepared the page for translation) |
||
| (No se muestran 7 ediciones intermedias de 3 usuarios) | |||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
<languages/> | |||
<translate> | |||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
[[File:1024px-0118Hot-mix asphalt concrete manual pouring-paving in the repair and maintenance 19.jpg|thumb|Hot asphalt mixer.]] | |||
*Tar is a product of the distillation of coal.<ref name="Bosse">Bosse GM, et al. Hot asphalt burns: a review of injuries and management options. Am J Emerg Med. 2014 Jul;32(7):820.e1-3.</ref> | *Tar is a product of the distillation of coal.<ref name="Bosse">Bosse GM, et al. Hot asphalt burns: a review of injuries and management options. Am J Emerg Med. 2014 Jul;32(7):820.e1-3.</ref> | ||
**Asphalt (now more commonly used than tar) and tar are both forms of ''bitumen'' | **Asphalt (now more commonly used than tar) and tar are both forms of ''bitumen'' | ||
| Línea 7: | Línea 12: | ||
*Tar/asphalt is highly viscous and sticks to skin, making it difficult to remove and leading to more severe burns | *Tar/asphalt is highly viscous and sticks to skin, making it difficult to remove and leading to more severe burns | ||
*Tar itself is sterile, but dead tissue underneath is not | *Tar itself is sterile, but dead tissue underneath is not | ||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
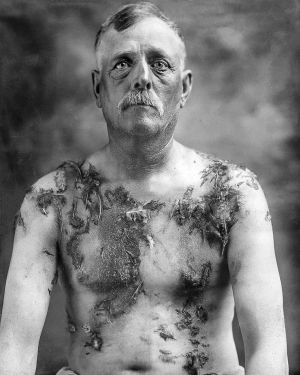
[[File:John Meintz, punished during World War I - NARA - 283633 (restored and edited v.2.).jpg|thumb|Mn who was "tarred and feathered."]] | |||
*Viscous black substance on skin in setting of history of working with coal tar or asphalt | *Viscous black substance on skin in setting of history of working with coal tar or asphalt | ||
**May be hardened or still relatively fluid on presentation to ED | **May be hardened or still relatively fluid on presentation to ED | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
</translate> | |||
{{Caustic burn types}} | {{Caustic burn types}} | ||
<translate> | |||
==Evaluation== | |||
*Clinical diagnosis | *Clinical diagnosis | ||
*Workup should be based on clinical presentation, and may include: | *Workup should be based on clinical presentation, and may include: | ||
**VBG, CBC, chem, total CK | **VBG, CBC, chem, total CK | ||
**[[CXR]] | **[[Special:MyLanguage/CXR|CXR]] | ||
**[[ECG]] | **[[Special:MyLanguage/ECG|ECG]] | ||
** | **[[Special:MyLanguage/Urinalysis|Urinalysis]] (assess for myoglobinuria) | ||
**Serial assessments for compartment syndrome | **Serial assessments for compartment syndrome | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Immediate treatment | *Immediate treatment | ||
**Cool tar with cold water until hardened to stop burning and limit tissue damage | **Cool tar with cold water until hardened to stop burning and limit tissue damage | ||
| Línea 33: | Línea 49: | ||
**Neosporin ointment has a petroleum base and is successful at slowly dissolving tar/asphalt (may also help prevent infection)<ref name="Bosse" /> | **Neosporin ointment has a petroleum base and is successful at slowly dissolving tar/asphalt (may also help prevent infection)<ref name="Bosse" /> | ||
**Mineral oil has also been identified as a safe, non-toxic, and effective means of dissolving tar/asphalt<ref name="Carta">Carta T, et al. Use of mineral oil Fleet enema for the removal of a large tar burn: a case report. Burns. 2015 Mar;41(2):e11-4.</ref> | **Mineral oil has also been identified as a safe, non-toxic, and effective means of dissolving tar/asphalt<ref name="Carta">Carta T, et al. Use of mineral oil Fleet enema for the removal of a large tar burn: a case report. Burns. 2015 Mar;41(2):e11-4.</ref> | ||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
*Admit or transfer to burn center for: | *Admit or transfer to burn center for: | ||
**>10% TBSA (>5% for full thickness injury) | **>10% [[Special:MyLanguage/TBSA|TBSA]] (>5% for full thickness injury) | ||
**Burns of face, eyes, ears, genitalia, joints | **Burns of face, eyes, ears, genitalia, joints | ||
**Circumferential burns | **Circumferential burns | ||
**Airway involvement | **Airway involvement | ||
**Significant comorbidity | **Significant comorbidity | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Burns]] | |||
*[[Special:MyLanguage/Burns|Burns]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| Línea 51: | Línea 73: | ||
[[Category:GI]] | [[Category:GI]] | ||
[[Category:Toxicology]] | [[Category:Toxicology]] | ||
[[Category:Trauma]] | |||
</translate> | |||
Revisión actual - 00:00 5 ene 2026
Background
- Tar is a product of the distillation of coal.[1]
- Asphalt (now more commonly used than tar) and tar are both forms of bitumen
- Currently used mainly for roofing and road paving
- When used for these purposes, tar/asphalt is heated to between 140-190°C (for paving) and 210-270°C (for roofing)[1]
- Injuries limited almost exclusively to occupational exposure in these fields
- Tar/asphalt is highly viscous and sticks to skin, making it difficult to remove and leading to more severe burns
- Tar itself is sterile, but dead tissue underneath is not
Clinical Features
- Viscous black substance on skin in setting of history of working with coal tar or asphalt
- May be hardened or still relatively fluid on presentation to ED
Differential Diagnosis
Caustic Burns
- Caustic ingestion
- Caustic eye exposure (Caustic keratoconjunctivitis)
- Caustic dermal burn
- Airbag-related burns
- Hydrofluoric acid
- Tar burn
- Cement burn
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis
- Workup should be based on clinical presentation, and may include:
- VBG, CBC, chem, total CK
- CXR
- ECG
- Urinalysis (assess for myoglobinuria)
- Serial assessments for compartment syndrome
Management
- Immediate treatment
- Cool tar with cold water until hardened to stop burning and limit tissue damage
- Take care to avoid hypothermia
- Removal of tar/asphalt (unless small area, will generally occur in inpatient setting)
- Needs to be dissolved as manual debridement of hardened tar/asphalt damages underlying tissue[2]
- The best solvents are chemically similar to tar/asphalt ("like dissolves like") - suggested agents include baby oil, sunflower oil, butter, and mayonnaise[2][1]
- Neosporin ointment has a petroleum base and is successful at slowly dissolving tar/asphalt (may also help prevent infection)[1]
- Mineral oil has also been identified as a safe, non-toxic, and effective means of dissolving tar/asphalt[3]
Disposition
- Admit or transfer to burn center for:
- >10% TBSA (>5% for full thickness injury)
- Burns of face, eyes, ears, genitalia, joints
- Circumferential burns
- Airway involvement
- Significant comorbidity
See Also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Bosse GM, et al. Hot asphalt burns: a review of injuries and management options. Am J Emerg Med. 2014 Jul;32(7):820.e1-3.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Iuchi M, et al. The comparative study of solvents to expedite removal of bitumen. Burns. 2009 Mar;35(2):288-93.
- ↑ Carta T, et al. Use of mineral oil Fleet enema for the removal of a large tar burn: a case report. Burns. 2015 Mar;41(2):e11-4.