Diferencia entre revisiones de «Periorbital cellulitis»
(Created page with "===Background=== *Must distinguish between these orbital and periorbital cellulitis! **See Periorbital vs Orbital Cellulitis *Periorbital cellulitis most often 2/2 contiguous...") |
Sin resumen de edición |
||
| (No se muestran 27 ediciones intermedias de 8 usuarios) | |||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
==Background== | |||
[[File:Orbital septum slide - final big gallery.jpeg|thumb|Periorbital anatomy.]] | |||
*Also known as "preseptal cellulitis" | |||
* | *Most often due to contiguous infection of soft tissues of face and eyelids | ||
* | *Most patients are <10yr | ||
*Rarely leads to orbital cellulitis | |||
== | ===Periorbital vs Orbital Cellulitis=== | ||
=== | {{Periorbital vs orbital cellulitis}} | ||
==Clinical Features== | |||
[[File:PMC3214412 IJO-59-431-g007.png|thumb|Periorbital cellulitis]]. | |||
*Swelling, tenderness, and erythema of eyelids and superficial tissues surrounding the orbit | |||
*+/- [[fever]] | |||
*'''Lack of''': | |||
**[[Proptosis]] | |||
**[[red eye|Chemosis]] | |||
**Globe displacement | |||
**Limitation of eye movements | |||
**Pain with eye movement | |||
**[[diplopia|Double vision]] | |||
**[[Vision loss]] (indicates orbital apex involvement) | |||
=== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
{{Periorbital swelling DDX}} | |||
== | ==Evaluation== | ||
[[File:RtmaxobitinfectteethCT.png|thumb|Periorbital cellulitis caused by a dental infection (also causing maxillary [[sinusitis]]).]] | |||
*CT Orbit with IV contrast if: | |||
**Concern for orbital cellulitis-i.e. equivocal assessment of proptosis, red eye, EOM function or pain w/ eye movement | |||
**Unable to accurately assess vision (e.g. age <1yr) | |||
==Management== | |||
{{Periorbital Cellulitis Antibiotics}} | |||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
*If well-appearing and afebrile consider discharge | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Línea 40: | Línea 42: | ||
*[[Orbital Cellulitis]] | *[[Orbital Cellulitis]] | ||
== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:ID]] | [[Category:ID]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Ophthalmology]] | ||
Revisión actual - 22:31 23 oct 2024
Background
- Also known as "preseptal cellulitis"
- Most often due to contiguous infection of soft tissues of face and eyelids
- Most patients are <10yr
- Rarely leads to orbital cellulitis
Periorbital vs Orbital Cellulitis
- Orbital cellulitis may mimic periorbital cellulitis early in its course
- Orbital cellulitis
- Ocular emergency
- Most often due to ethmoid sinusitis
- May also be due to orbital trauma, endophthalmitis, infection from teeth / middle ear
- Not caused by extension of periorbital cellulitis
- Periorbital cellulitis
- Usually benign
- Most often due to contiguous infection of soft tissues of face and eyelids
Clinical Features
.
- Swelling, tenderness, and erythema of eyelids and superficial tissues surrounding the orbit
- +/- fever
- Lack of:
- Proptosis
- Chemosis
- Globe displacement
- Limitation of eye movements
- Pain with eye movement
- Double vision
- Vision loss (indicates orbital apex involvement)
Differential Diagnosis
Periorbital swelling
Proptosis
- Normal IOP
- Orbital cellulitis
- Orbital pseudotumor
- Orbital tumor
- Increased IOP
- Retrobulbar abscess
- Retrobulbar emphysema
- Retrobulbar hemorrhage
- Ocular compartment syndrome
- Orbital tumor
No proptosis
- Periorbital cellulitis/erysipelas
- Dacryocystitis (lacrimal duct)
- Dacryocele/Dacryocystocele
- Dacryostenosis
- Dacryoadenitis (lacrimal gland)
- Allergic reaction
- Nephrotic Syndrome (pediatrics)
Lid Complications
- Blepharitis (crusts)
- Chalazion (meibomian gland)
- Stye (hordeolum) (eyelash folicle)
Other
- Subperiosteal abscess
- Orbital abscess
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Conjunctivitis
- Contact dermatitis
- Herpes zoster
- Herpes simplex
- Sarcoidosis
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Evaluation
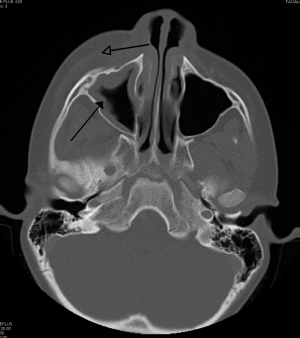
- CT Orbit with IV contrast if:
- Concern for orbital cellulitis-i.e. equivocal assessment of proptosis, red eye, EOM function or pain w/ eye movement
- Unable to accurately assess vision (e.g. age <1yr)
Management
Antibiotics
Outpatient
Treatment recommended for 5-7 days. If signs of cellulitis persist at the end of this period, treatment should be continued until the eyelid erythema and swelling have resolved or nearly resolved.
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 1-2 double-strength tablets BID OR
- In children: 8 to 12 mg/kg QD of the TMP component divided every 12 hours
- Clindamycin 300mg Q8H
- In children: 30 to 40 mg/kg per day in three to four equally divided doses, maximum 1.8 grams per day
PLUS one of the following agents:
- Amoxicillin 875 mg BID OR
- In children: usual dosing is 45 mg/kg per day divided every 12 hours; dosing for severe infections or when penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae is a concern (using the 600 mg/5 mL suspension) is 90 mg/kg per day divided every 12 hours
- Cefpodoxime 400mg BID OR
- In children <12 years of age: 10 mg/kg per day divided every 12 hours, usual maximum dose 200 mg; in children ≥12 years and adolescents: 400 mg every 12 hours
- Cefdinir 300 mg BID
- In children: 14 mg/kg per day, divided every 12 hours, maximum daily dose 600 mg
Inpatient
Vancomycin 15-20mg/kg IV BID + (one of the following)
- Ampicillin/Sulbactam 3 g IV q6hr OR
- Ticarcillin/Clavulanate 3.1 g IV q4h OR
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam 4.5 g IV q6h OR
- Ceftriaxone 2 g IV q12hr OR
- Cefotaxime 2 g IV q4h
Disposition
- If well-appearing and afebrile consider discharge




